Cryptorchidism In Boys: Do You Know What It Is?
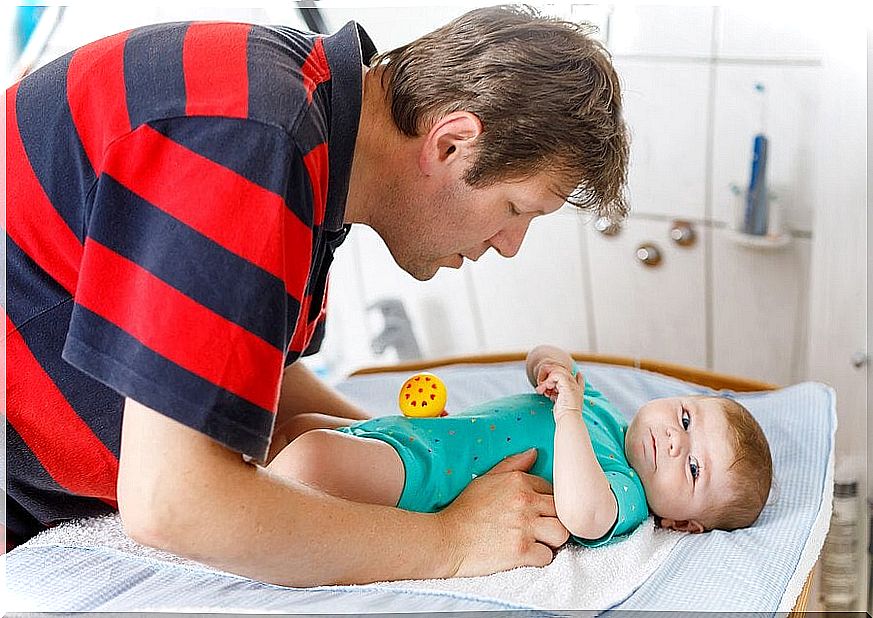

Cryptorchidism is a genital problem related to a non-descending or poorly descended testicle. If not treated in time, it can be extremely harmful to the child in the future.
This genital developmental disorder is not shown on prenatal ultrasound before 28 weeks’ gestation. For this reason, to detect it early, a transinguinal migration must be performed.
What are the causes of the appearance of cryptorchidism?
Cryptorchidism is one of the most common disorders in children and its onset factors are very varied; for there is no exact cause.
These are some of the most frequent elements that indicate that a child may be suffering from this disorder:
- Low birth weight: this happens mainly when the baby has a premature birth. Weight is considered low when it is less than 2.5 kg.
- Premature birth: these are cases in which the baby is born before the mother reaches 37 weeks of gestation.
- Small size for gestational age: the baby is considered smaller than it should be.
- Maternal exposure to estrogen during the first month of pregnancy: This is due to normal physical changes that occur during the first month of pregnancy.
- Intra-abdominal pressure: refers to the pressure that occurs within the abdominal cavity above 10 centimeters.
- Abdominal wall malformations: is a group of congenital malformations that represent heterogeneous defects that cause herniation or evisceration of one or more organs in the abdominal cavity.

cryptorchidism diagnosis
The most common way to find out the diagnosis of this disorder is through a doctor’s examination and evaluation. This is done by palpating the scrotum.
If the sac is empty, the index finger touches the caudal inguinal canal from top to bottom to confirm that the testicle is on its way. If the testicles do not descend correctly or are ectopic, the probability of detecting it will be 80%.
This assessment should be performed routinely and, although it is very effective, what is known as false cryptorchidism, which is caused by a cremasteric reflex , can occur. Thus, occasionally an abdominal ultrasound, a CT or MRI scan may be performed to locate the testicle.
Types of cryptorchidism
There are different types of cryptorchidism. The pediatrician, according to his assessment, will be in charge of determining the treatment to be followed, depending on the results.
These are the existing types:
- Elevated testis: this is reflected when the testis is not in the scrotum but can be manually lowered ; requires continuous evaluation.
- Ectopic Testis: Occurs when the testis is outside the inguinal canal; usually appears in the subcutaneous location.
- Acquired non-descending testicles: at first they were not in the scrotum but descend during the first year of life and then come back up. This type of disorder requires follow-up until 10 years of age.
- Missing Testicles: In this type of disorder, the testicle is not in the scrotum or in the inguinal canal or abdomen. In that case, an ultrasound or surgical exploration is required.
- True cryptorchidism: occurs when the testicle is not in the scrotum and can be felt in the inguinal canal; but it is not possible to bring it down.
cryptorchidism treatment
Most cryptorchidism resolves spontaneously in the first year, so it is recommended to just observe the child and periodically check that the testicles descend on their own. If this does not happen after one year of age, treatment should be considered, which can be hormonal or surgical.
Hormonal treatment
Currently, this treatment is less common. It consists of the intramuscular administration of a hormone that favors the descent of the testicle into the scrotum.
Its downside is that its results are not always effective; because probably after therapy the testicle will go up again. Furthermore, this type of treatment is not free from side effects.

Surgical treatment
This is the most effective treatment today. It consists of descending the testicle into the scrotum through an intervention called orchidopexy. It is recommended that it be done before 18 months of age; the chances of success of this intervention are quite high.
Complications of cryptorchidism
If this disorder is not treated in time, it can greatly affect the child’s health. So, it is recommended to act quickly in case you suspect that the child has this anomaly in their genital area.
These are some of the complications that can occur:
- Infertility.
- Increased risk of getting testicular cancer.
- Testicular torsion.
- Inguinal hernia.
Cryptorchidism can be really harmful to boys if it is not treated in time. Therefore, parents should pay special attention if the child is suspected of suffering from this disorder. Communicating quickly with the GP will allow for relevant controls.